- Home
- Security & Compliance
- Mastering Azure Policies: Enforce Your Governance with Ease🔐
Mastering Azure Policies: Enforce Your Governance with Ease🔐
Take Control of Your Cloud: How Azure Policies Simplify Governance
As businesses scale their cloud infrastructure, maintaining control and ensuring compliance can become increasingly challenging. This is where Azure Policies come into play, helping organizations govern resources and enforce rules efficiently. Whether you’re aiming to optimize costs, secure environments, or ensure compliance, Azure Policies have you covered. Let’s dive into how they work and why they should be a cornerstone of your cloud strategy. 🚀
What Are Azure Policies? 🤔
At its core, Azure Policy is a service designed to help you create, assign, and manage policies that enforce rules over your resources. These policies ensure your resources stay compliant with your corporate standards and SLAs (Service Level Agreements). Azure Policy works at a subscription level, offering real-time evaluation and compliance reporting. 🎯
Unlike Role-based Access Control (RBAC), which focuses on managing user permissions, Azure Policy works at the resource level, enforcing rules that resources must follow.
Why Azure Policies Matter 🛡️
Managing cloud infrastructure in a consistent manner is vital to:
- Enforce compliance: Ensure resources comply with regulations (e.g., ISO, GDPR) and organizational policies.
- Minimize security risks: Keep your environment secure by enforcing key security measures like encryption, network configurations, or the use of specific VM sizes.
- Cost control: Block costly resources or specific SKUs that could inflate cloud expenses.
Azure Policies allow you to enforce these rules automatically, so you don’t need to manually audit resources. 📊
Key Components of Azure Policy 🛠️
To fully utilize Azure Policy, it’s essential to understand its building blocks:
Policy Definition 📝
- This is where you define your rules. A policy could be as simple as restricting the region where VMs can be created, or as complex as requiring tags on all resources for better cost allocation.
Policy Assignment 📌
- Once you’ve created a policy, it needs to be assigned to specific scopes like a subscription, resource group, or management group. Assigning a policy means it will enforce its rule across the specified scope.
Policy Parameters 🎛️
- Many policies are customizable through parameters. For example, you could create a policy that restricts VMs to certain sizes but allows the actual size to be defined at the time of assignment.
Initiatives (Policy Set) 🧩
- When managing large environments, you may want to group multiple policies into an initiative. This allows for the management of a broader set of governance objectives under a single umbrella. 🌐
Compliance Reporting 📈
- Azure Policy provides built-in compliance tracking. After assigning a policy, you can easily view which resources are compliant or non-compliant, allowing you to take corrective action.
Top Use Cases for Azure Policy 📋
- Enforcing Resource Tags 🏷️Tagging resources is a best practice for cost management and resource tracking. With Azure Policy, you can enforce a rule that requires resources to have specific tags, like “Department” or “CostCenter.” If someone forgets to add a tag, Azure Policy will either add it automatically or flag the resource as non-compliant.
- Restricting Resource Regions 🌍Sometimes, you may want to restrict the regions where resources can be created. For example, if your organization operates solely within the EU, you can create a policy that ensures all resources are deployed within European regions. ❌🗺️
- Control Resource Sizing 📦Oversizing VMs can drive up cloud costs unnecessarily. You can implement policies to limit the VM sizes your teams can deploy, helping keep costs in check while ensuring performance. 🚦💸
- Ensure Data Encryption 🔒 To ensure compliance with security standards, you can use Azure Policies to enforce data encryption. Any storage accounts or VMs without encryption can be flagged or even prevented from being created. 🛡️
- Audit Unused Resources 🕵️♂️ If you want to keep track of unused or underutilized resources, Azure Policy can audit and flag such resources. For instance, you can define a policy that flags VMs with CPU usage below a certain threshold over a defined period. 📊
Getting Started with Azure Policy 🚀
Setting up Azure Policy is simple. Here’s a quick guide to configure an “Allowed Location” policy for your resources(You can use Prebuilt Policy Definition for this) :
Step 1: Create a Policy Definition 📐
1. Head over to the Azure Portal and search for Policy.
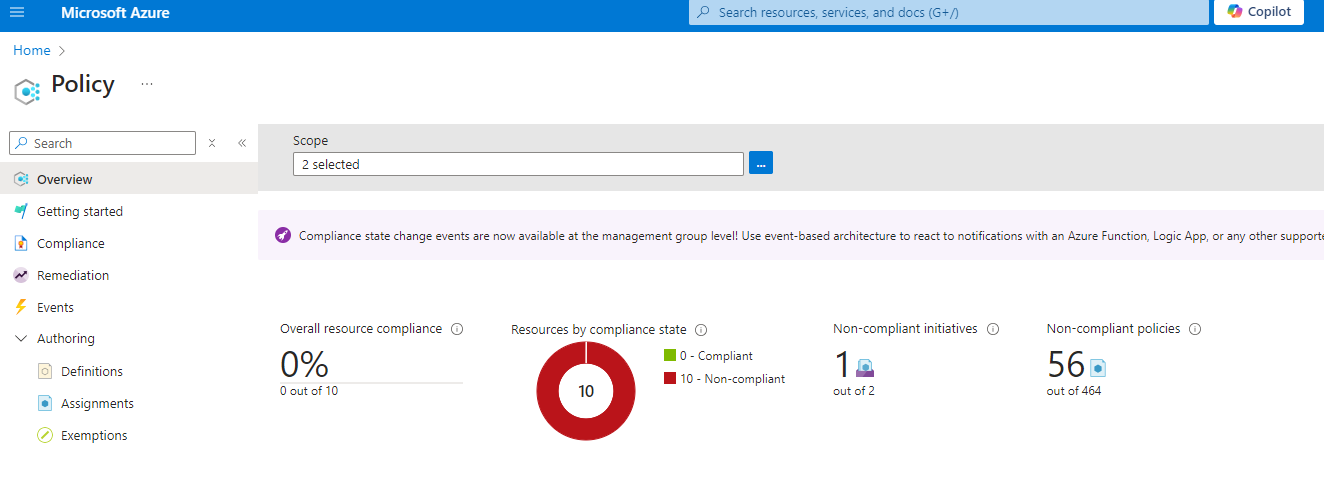
2. Select Definitions from the sidebar and click + Search ->Location and Click Allowed Locations
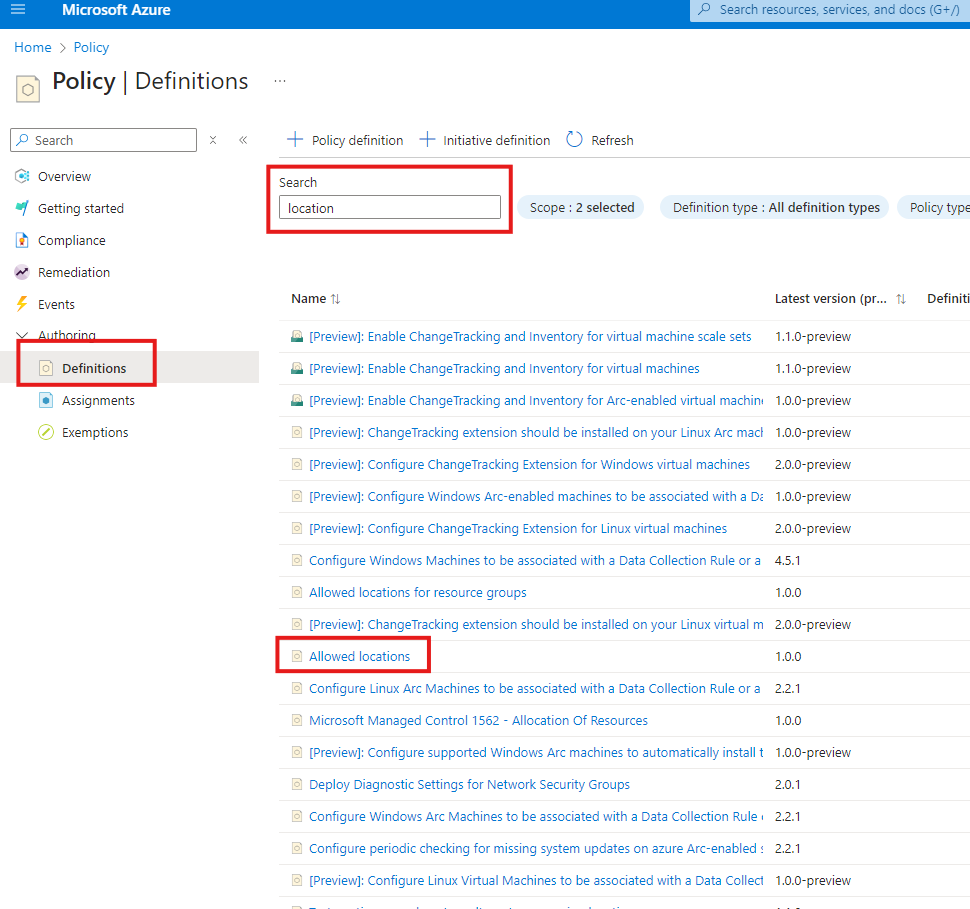
3. Select your Scope, It can be the whole Subscription or One Resource group and Click Next
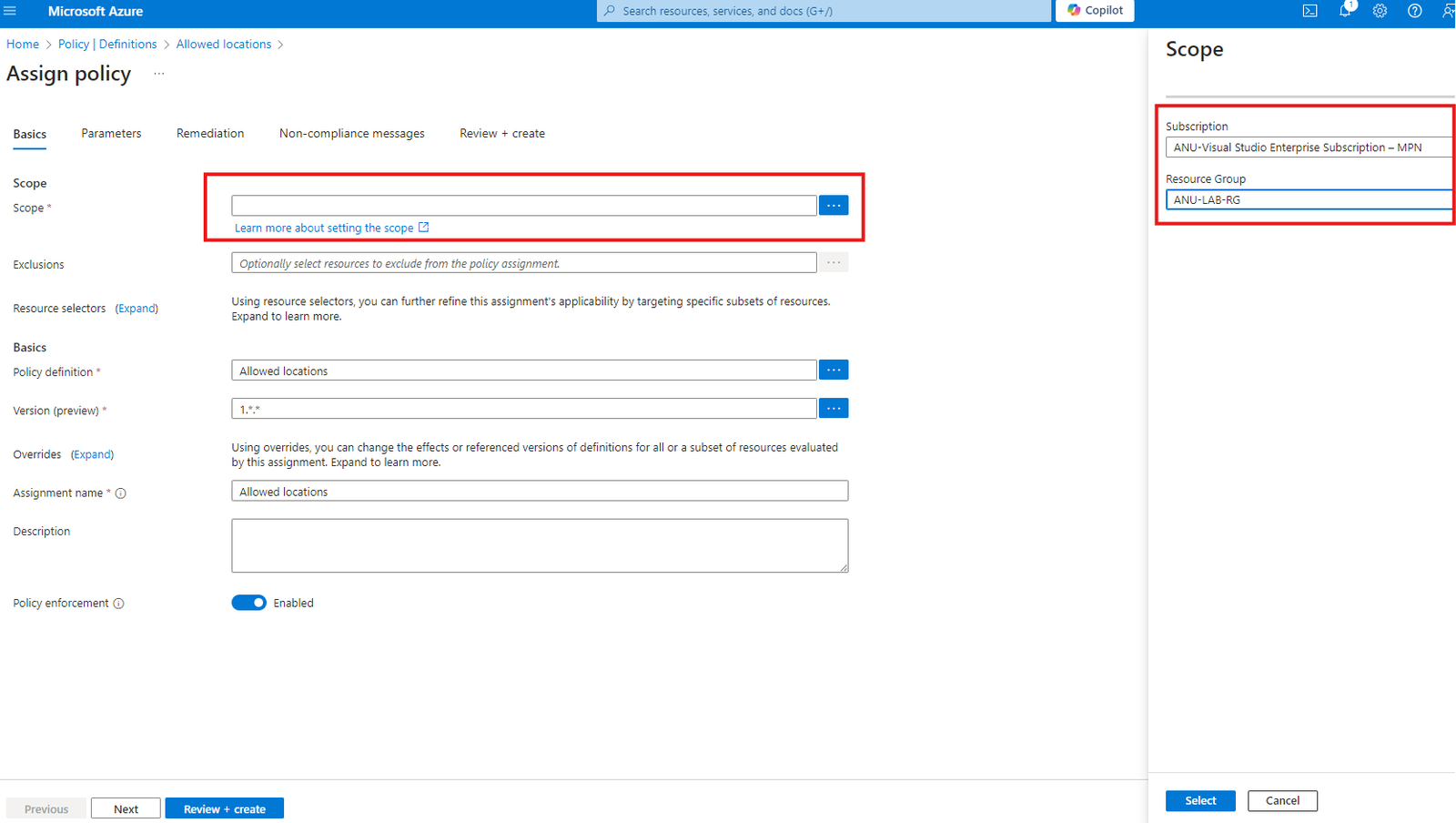
4. In the Parameters Section you can select Allowed location, in my case I set allowed location Only “UAE North” and Click Next
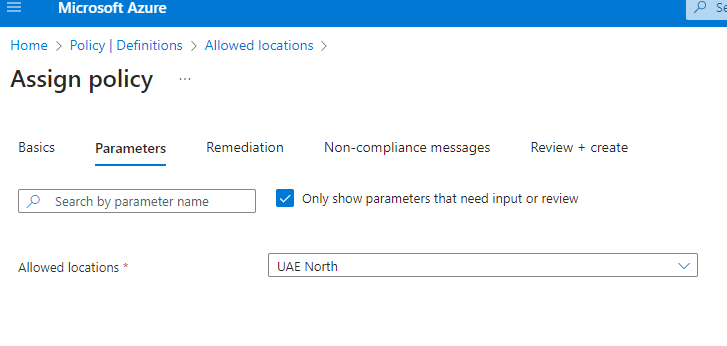
5. In the next tab “Remediation” – By default, this assignment will only take effect on newly created resources. Existing resources can be updated via a remediation task after the policy is assigned. For deployIfNotExists policies, the remediation task will deploy the specified template. For modify policies, the remediation task will edit tags on the existing resources.
so for my case I do not want to Remediate my old resources as per this policy I keep this option as it is and Click next
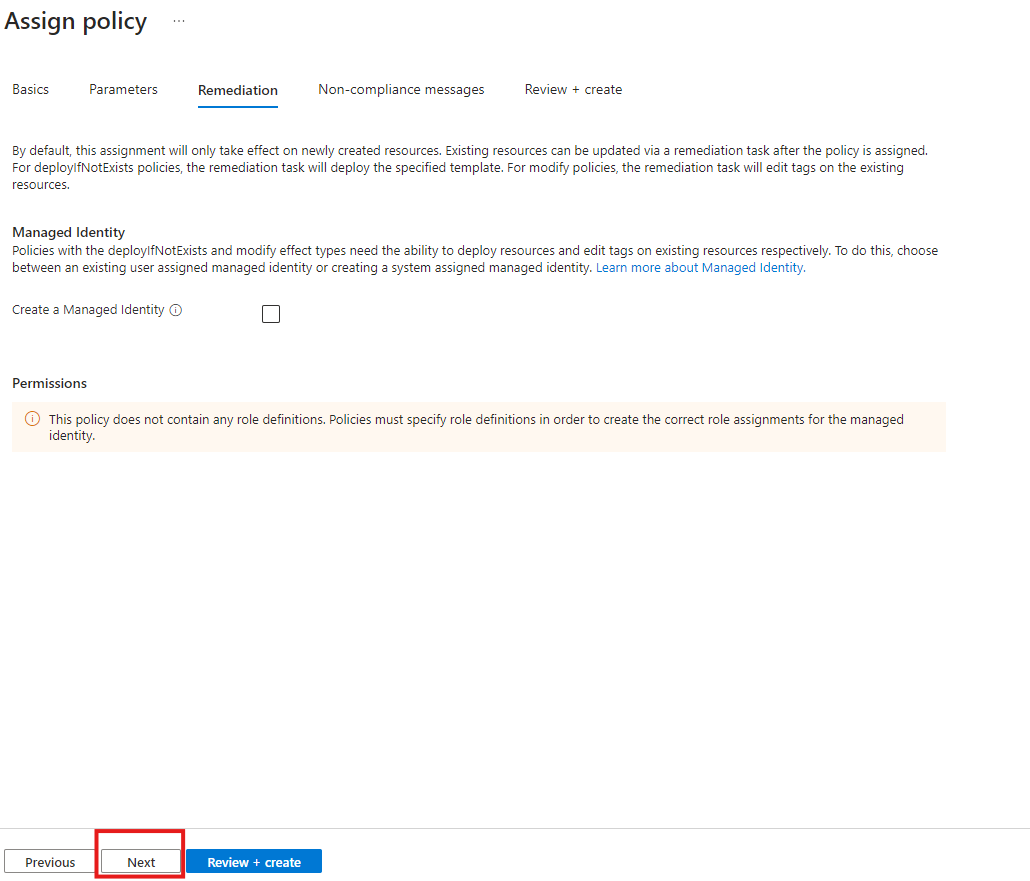
6. In the Non-Compliance Tab where we configure the Massage that user will gets if he deployed the resources in Non compliance Locations and Click Next
7. Review and Create
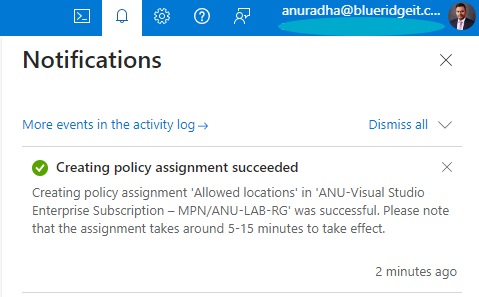
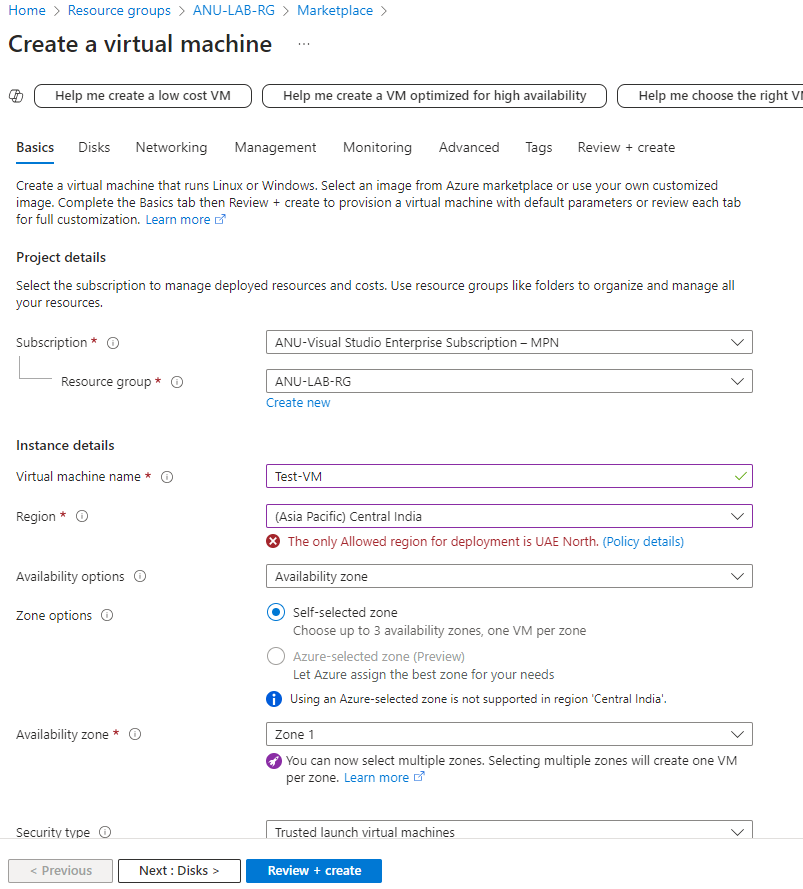
Test Drive 🕵️♂️
According to the test results below, selecting the Central India location results in an error – “The only Allowed region for deployment is UAE North.”
Best Practices for Using Azure Policies ✅
- Start with built-in policies: Azure offers a wide range of built-in policies that can address common governance needs. Start with these and then customize as necessary.
- Use initiatives for broader coverage: Group multiple policies into an initiative to tackle more complex governance requirements across your organization.
- Monitor compliance regularly: Make sure to routinely check compliance reports and act on any non-compliant resources to maintain governance standards.
Wrapping Up: Automate and Simplify Governance 🛠️🤖
Azure Policies are a powerful tool to automate governance and ensure that your cloud environment remains compliant, secure, and optimized. Whether you’re just getting started with Azure or managing a large-scale cloud deployment, leveraging Azure Policy is essential for maintaining control and reducing risks.


Link alternatif Login gotobet88
July 6, 2025I’m truly enjoying the design and layout of your website.
It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more enjoyable for me to come
here and visit more often. Did you hire out a developer to create your theme?
Superb work!